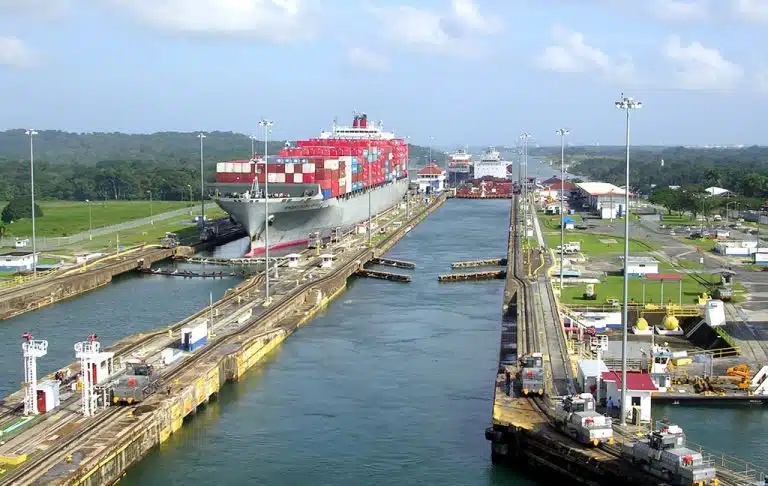
The Panama Canal, an essential artery of global trade, has recently faced the challenge of decreased ship crossings due to low water levels. This phenomenon has disrupted supply chains worldwide and led to increased transportation costs. However, despite the significant decline in ship traffic, the Panama Canal has managed to avoid a financial crisis, maintaining its stability and continuing to contribute to Panama’s economy.
The reduction in ship crossings was primarily driven by lower water levels, which forced officials to implement restrictions on the number of vessels passing through the canal. This limitation disrupted the flow of goods and commodities, impacting businesses and industries reliant on timely deliveries. Consequently, concerns arose about the financial implications for the Panama Canal, given its dependence on toll revenue for operational sustainability and its contribution to the national economy.
Remarkably, the Panama Canal has demonstrated resilience in the face of adversity. Despite the decrease in ship traffic, the canal has not experienced a significant downturn in its financial performance. This resilience can be attributed to several key factors:
Diversified Revenue Streams: While toll revenue from ship crossings is a primary source of income for the Panama Canal, it is not the sole revenue stream. The canal also generates revenue from various auxiliary services, including pilotage, towing, and water services. By diversifying its revenue sources, the canal has reduced its reliance on ship crossings alone, mitigating the impact of decreased traffic.
Efficient Cost Management: The management of operational costs plays a crucial role in maintaining financial stability. The Panama Canal has implemented measures to optimize operational efficiency and minimize expenses, ensuring that it remains financially viable even during periods of reduced activity. Strategic cost management practices have enabled the canal to weather fluctuations in demand while preserving its financial health.
Long-Term Planning and Investment: The Panama Canal Authority (ACP) has adopted a forward-thinking approach to infrastructure development and maintenance. Investments in modernization projects, such as the expansion of the canal with the construction of the new locks, have enhanced its capacity and competitiveness in the global shipping industry. By continuously investing in its infrastructure and technology, the canal has positioned itself to adapt to changing market conditions and sustain its financial performance.
Flexibility and Adaptability: In response to the challenges posed by low water levels and reduced ship crossings, the Panama Canal has demonstrated flexibility in its operations. The implementation of measures to optimize transit schedules, prioritize cargo, and manage water resources has enabled the canal to navigate through periods of adversity without compromising its financial stability. Additionally, the canal has explored innovative solutions, such as water-saving measures and efficiency enhancements, to mitigate the impact of climate-related challenges on its operations.
Despite the disruption caused by decreased ship crossings, the Panama Canal has remained financially resilient, underscoring its significance as a critical conduit of global trade. As the canal continues to navigate through challenges such as climate variability and shifting market dynamics, its ability to adapt, innovate, and sustain financial stability will be essential in ensuring its continued role as a linchpin of international commerce. By leveraging its strengths, diversifying its revenue streams, and investing in its future, the Panama Canal is well-positioned to overcome obstacles and maintain its status as a vital lifeline of global trade.